When it comes to the food and agribusiness industry, success isn’t just about producing and selling products. It’s about navigating a complex and ever-changing landscape while ensuring that your operations are sustainable, profitable, and competitive. In this article, we’ll explore ten proven strategies that can help you achieve success in food and agribusiness management.
Read, Also >>>>> Discover The Top 10 Common Plant Diseases in Organic Farming and How to Beat Them
1. Embrace Sustainability
Embrace Sustainability in Food and Agribusiness Management
In today’s rapidly changing world, sustainability has become a top priority across industries, and the food and agribusiness sector is no exception. Embracing sustainability isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity for long-term success. In this section, we’ll delve deeper into what sustainability means in the context of food and agribusiness management and why it’s crucial.

Understanding Sustainability in Agribusiness
At its core, sustainability in agribusiness involves managing agricultural practices and the entire supply chain in a way that meets the current needs of consumers and businesses without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. It’s about finding a balance between economic profitability, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility.
Here are some key aspects of sustainability in food and agribusiness:
Environmental Stewardship:
This includes minimizing the environmental impact of agricultural operations. It involves practices such as reducing water usage, conserving energy, and using eco-friendly farming techniques. For example, adopting precision agriculture can help reduce water wastage by targeting irrigation only where it’s needed.
Economic Viability:
Sustainability should make economic sense. While it may involve some upfront costs, it often leads to long-term savings. Sustainable practices can reduce input costs, increase yields, and open up new market opportunities. For instance, organic farming methods may initially require more labor, but they can command higher prices in the market.
Social Responsibility:
Ensuring the well-being of farmworkers, communities, and consumers is a vital aspect of sustainability. Fair labor practices, community engagement, and providing access to healthy food options all contribute to social sustainability.
Why Embrace Sustainability in Agribusiness?
Market Demand: Consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impacts of their food choices. Sustainable products are in high demand, and businesses that can meet this demand gain a competitive edge.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regions are implementing stricter regulations on agriculture, particularly concerning water usage, pesticide use, and waste management. Embracing sustainability ensures your business remains compliant with evolving laws.
Resource Scarcity: As the global population grows, resources like water and arable land are becoming scarcer. Sustainable practices help optimize resource use and ensure long-term availability.
Risk Mitigation: Sustainable practices can help mitigate risks associated with climate change, such as extreme weather events and shifting growing seasons.
Implementing Sustainability Strategies
To embrace sustainability effectively, consider these strategies:
- Environmental Audits: Regularly assess your environmental impact and set targets for improvement.
- Certifications: Obtain certifications such as USDA Organic or Fair Trade to demonstrate your commitment to sustainability.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Know your suppliers and encourage sustainable practices throughout your supply chain.
- Education and Training: Train your workforce in sustainable practices and keep them updated on the latest developments.
- Innovation: Invest in research and development to find new ways to reduce your environmental footprint.
Embracing sustainability isn’t just a responsibility; it’s an opportunity. By integrating sustainable practices into your food and agribusiness management, you not only contribute to a healthier planet but also position your business for long-term success in an increasingly conscious marketplace.
2. Invest in Technology
Investing in Technology for Food and Agribusiness Management
In the rapidly evolving landscape of food and agribusiness management, staying ahead of the curve often requires a proactive approach to technology adoption. Incorporating advanced technologies into your agricultural operations can enhance productivity, improve decision-making, and drive long-term success. In this section, we’ll explore the significance of investing in technology and how it can benefit your agribusiness.

The Role of Technology in Agribusiness
Technology has become an integral part of modern agriculture, revolutionizing traditional farming practices and supply chain management. Here’s why investing in technology is essential for agribusiness management:
Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture leverages technologies such as GPS, sensors, and drones to optimize crop management. It allows for precise planting, irrigation, and fertilization, reducing resource wastage and increasing yields.
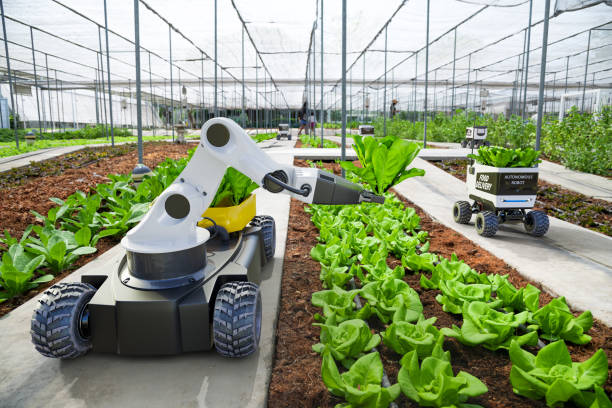

Data-Driven Insights: Modern farming generates vast amounts of data. Utilizing data analytics tools can help you make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and resource allocation. For instance, analyzing historical weather data can aid in predicting optimal planting times.
Farm Management Software: Implementing farm management software streamlines various tasks, from inventory tracking to labor management. These tools enhance efficiency and reduce administrative overhead.
IoT and Smart Farming: The Internet of Things (IoT) enables real-time monitoring of farm conditions. IoT sensors can track soil moisture, temperature, and livestock health, allowing for timely interventions.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability in the supply chain. It’s particularly valuable for verifying product origins and ensuring food safety.
Farm Automation: Automated machinery and robotic systems can handle repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs and minimizing human error.

Benefits of Technology Adoption
Investing in technology can yield a multitude of benefits for your food and agribusiness:
Increased Productivity: Automation and data-driven insights lead to higher crop yields and more efficient resource utilization.
Cost Savings: Technology can help reduce operational costs by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste.
Improved Quality: Precise control over farming practices can result in higher product quality, which often commands premium prices.
Sustainability: Many agribusiness technologies support sustainable practices, such as efficient water usage and reduced pesticide application.
Market Competitiveness: Embracing technology can set your agribusiness apart from competitors, attracting tech-savvy consumers and partners.
Implementing Technology Strategies
To effectively invest in technology, consider these steps:

Assessment: Evaluate your specific needs and challenges to determine which technologies align with your goals.
Education: Train your workforce to use new technologies effectively.
Start Small: Begin with pilot projects to minimize risks and learn from initial deployments.
Partnerships: Collaborate with tech providers and industry experts to stay updated on emerging technologies.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly assess the performance of your technology investments and make adjustments as needed.
Technology is a driving force in the modern food and agribusiness landscape. Embracing technology isn’t just an option; it’s a necessity for long-term success. By investing in precision agriculture, data analytics, automation, and other cutting-edge solutions, you can position your agribusiness for greater efficiency, profitability, and competitiveness in the dynamic agribusiness sector.
3. Optimize Supply Chain Management
Optimizing Supply Chain Management in Food and Agribusiness
Efficient supply chain management is a critical component of successful food and agribusiness management. It’s the backbone that ensures your products move seamlessly from farm to market, and any disruptions can have significant financial and operational consequences. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of optimizing supply chain management and strategies to achieve it.

Understanding the Agribusiness Supply Chain
The agribusiness supply chain is a complex network involving numerous stakeholders, from farmers and suppliers to distributors and retailers. It encompasses the flow of goods, information, and finances. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the key stages:
Production: This stage involves activities like planting, cultivating, and harvesting crops, as well as raising livestock.
Processing: After the initial production phase, raw agricultural products are processed into various forms, such as packaged food products or bulk commodities.
Distribution: Products are transported to distribution centers, warehouses, and retail outlets.
Retail: The final stage involves selling the products to consumers through various channels, including brick-and-mortar stores and e-commerce platforms.
The Significance of Supply Chain Optimization
Effective supply chain management offers numerous advantages for food and agribusiness management:
Cost Reduction: Streamlining the supply chain minimizes unnecessary costs, such as excess inventory and transportation expenses.
Improved Efficiency: Optimizing processes reduces lead times, ensuring products reach the market faster.
Enhanced Quality Control: Monitoring and managing the supply chain helps maintain product quality and safety standards.
Better Customer Service: Timely deliveries and product availability lead to satisfied customers.
Risk Mitigation: A well-managed supply chain can better withstand disruptions caused by factors like weather, transportation issues, or market fluctuations.
Strategies for Supply Chain Optimization
Now, let’s delve into strategies to optimize your agribusiness supply chain:
Demand Forecasting: Accurate forecasting helps you anticipate market demand and adjust production accordingly, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking.
Inventory Management: Implement just-in-time inventory practices to minimize storage costs while ensuring products are readily available.
Supplier Relationships: Nurture strong relationships with suppliers to secure reliable sources of inputs and negotiate favorable terms.
Transportation Efficiency: Evaluate transportation options to minimize costs and delivery times. This may include optimizing routes or using alternative transportation modes.
Technology Integration: Invest in supply chain management software to track and manage inventory, orders, and logistics in real time.
Quality Assurance: Implement rigorous quality control standards at every stage of the supply chain to reduce waste and maintain product integrity.
Sustainability Initiatives: Incorporate sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon emissions in transportation or using eco-friendly packaging materials.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly analyze supply chain performance data and seek opportunities for further optimization.
Optimizing supply chain management is a cornerstone of successful food and agribusiness management. It ensures that your products are efficiently delivered to market, contributing to cost savings, quality control, and customer satisfaction. By implementing these strategies and staying agile in response to changing market dynamics, you can enhance your agribusiness’s competitiveness and resilience in a rapidly evolving industry.
4. Diversify Your Product Range
Diversifying Your Product Range in Food and Agribusiness
In the ever-evolving landscape of food and agribusiness management, diversification is a strategy that can open up new avenues for growth and reduce risk. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of diversifying your product range and how it can benefit your agribusiness.

Understanding Product Range Diversification
Diversification in agribusiness refers to expanding the types of products you produce or offer. Instead of relying solely on a single crop or product, diversifying involves branching out into different crops, livestock, or value-added products. The goal is to create a more resilient and profitable business by tapping into various market opportunities.
Why Diversify Your Product Range?
Diversification offers several compelling advantages for food and agribusiness management:
Risk Reduction: Relying on a single product or crop can leave your business vulnerable to market fluctuations, weather-related disasters, or disease outbreaks. Diversifying spreads risk, as poor performance in one area can be offset by success in another.
Market Expansion: By offering a broader range of products, you can appeal to a wider customer base and tap into different market segments. This can be particularly advantageous in responding to changing consumer preferences.
Seasonal Variability: Different crops or products have varying growing seasons and harvest times. Diversification can help maintain a more consistent revenue stream throughout the year.
Value-Added Opportunities: Diversifying into value-added products, such as processed foods or specialty goods, can yield higher profit margins compared to selling raw agricultural products.
Adaptation to Environmental Changes: Climate change and evolving environmental conditions may impact the suitability of certain crops or livestock in specific regions. Diversification allows you to adapt to these changes.
Strategies for Product Range Diversification
Now, let’s explore some strategies to effectively diversify your product range in food and agribusiness management:
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to identify emerging trends, consumer preferences, and underserved niches in the market.
Crop Rotation: Implement crop rotation practices to replenish soil nutrients and reduce the risk of soil degradation, while also diversifying your output.
Livestock Integration: If you primarily focus on crops, consider integrating livestock farming into your operation. Livestock can provide additional income streams through meat, dairy, or fiber products.
Value-Added Processing: Explore opportunities to add value to your products through processing or packaging. For example, you can turn fresh fruits into jams or sauces, or create artisanal cheese from milk.
Farm-to-Table Ventures: Consider selling directly to consumers through farmers’ markets, farm-to-table restaurants, or online platforms. This allows you to showcase a wider range of products and interact with customers.
Collaborations: Partner with other producers or agribusinesses to expand your product offerings. Cooperative ventures can lead to shared resources and increased market reach.
Sustainability Initiatives: Embrace sustainable farming practices and certifications, as these can open doors to markets focused on eco-friendly products.
Continuous Learning: Stay informed about advancements in agriculture and agribusiness. Attend industry events, workshops, and training programs to explore new opportunities.
Diversifying your product range is a strategic move that can enhance the resilience and profitability of your food and agribusiness. By carefully assessing market trends, managing risks, and exploring new product opportunities, you can position your business for long-term success in a dynamic and competitive industry.
5. Market Research and Consumer Insights
Market Research and Consumer Insights: Key Ingredients for Food and Agribusiness Success
In the fast-paced world of food and agribusiness management, staying ahead of the competition requires more than just producing quality products. It demands a deep understanding of your market and consumers. In this section, we’ll explore the pivotal role of market research and consumer insights and how they can propel your agribusiness to success.
The Power of Market Research
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including its size, trends, competitors, and potential customers. It serves as the foundation for informed decision-making in agribusiness management. Here’s why it’s essential:
Identifying Opportunities: Market research helps you uncover untapped market segments, emerging trends, and unmet consumer needs. It’s the compass that guides your business toward profitable directions.
Risk Mitigation: Understanding market dynamics and potential challenges allows you to proactively mitigate risks. It’s easier to navigate challenges when you anticipate them.
Product Development: Consumer feedback collected through market research can inform product development and refinement. This ensures that your offerings align with market demands.
Competitive Advantage: Staying informed about your competitors’ strategies and market positioning can help you identify gaps and differentiate your products or services.
Marketing Effectiveness: Market research informs your marketing efforts, enabling you to craft targeted campaigns that resonate with your audience.
Consumer Insights: Understanding Your Customers
Consumer insights go beyond market trends and delve into the minds and behaviors of your target audience. These insights help you tailor your products and marketing efforts to meet consumer preferences effectively. Here’s why consumer insights matter:
Personalization: Knowing your customers’ preferences allows you to create personalized experiences, from product recommendations to marketing messages.
Product Innovation: Understanding what consumers value and desire helps you innovate and develop products that resonate with them.
Customer Retention: Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal. Consumer insights enable you to build lasting relationships by addressing their needs and concerns.
Effective Communication: Tailored messaging that speaks to consumers’ pain points and aspirations is more likely to engage and convert.
Strategies for Market Research and Consumer Insights
Now, let’s explore strategies for effectively conducting market research and gaining consumer insights into food and agribusiness management:
Surveys and Questionnaires: Collect feedback directly from consumers through surveys or questionnaires. Ask about their preferences, buying habits, and pain points.
Focus Groups: Organize focus group discussions to gain in-depth insights into consumer perceptions and preferences.
Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics tools to mine valuable insights from sales data, website analytics, and social media interactions.
Competitor Analysis: Study your competitors’ strategies, pricing, and customer feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Trend Monitoring: Stay informed about industry trends, both locally and globally, to anticipate shifts in consumer behavior.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Implement CRM systems to track customer interactions and personalize marketing efforts.
Feedback Loops: Establish feedback mechanisms, such as customer service channels, to encourage customers to share their thoughts and concerns.
Market Segmentation: Segment your target market based on demographics, behavior, and preferences to create targeted marketing campaigns.
Market research and consumer insights are indispensable tools for achieving success in food and agribusiness management. By investing in these areas, you can make data-driven decisions, develop products that resonate with your audience, and build lasting relationships with satisfied customers. In a dynamic and competitive industry, understanding your market and consumers is the key to staying ahead.
6. Build Strong Partnerships
Building Strong Partnerships in Food and Agribusiness Management
In the world of food and agribusiness management, success often hinges on collaboration and building strong partnerships. These partnerships can range from suppliers and distributors to fellow farmers and industry stakeholders. In this section, we’ll explore the significance of building strong partnerships and how they can propel your agribusiness to new heights.

The Power of Strong Partnerships
Partnerships in agribusiness involve forming mutually beneficial relationships with other organizations or individuals. These partnerships can have a profound impact on your business. Here’s why they matter:
Resource Access: Collaborating with partners can provide access to critical resources such as raw materials, equipment, or expertise that may be otherwise challenging or costly to acquire.
Risk Mitigation: Sharing risks and responsibilities with partners can help distribute the burden of unforeseen challenges, such as weather-related disasters or market fluctuations.
Market Expansion: Partnerships can open doors to new markets, both locally and internationally, by leveraging the existing networks and customer bases of your partners.
Cost Reduction: Collaborating with partners can lead to cost savings through joint purchasing, shared marketing expenses, or economies of scale.
Innovation: Partnering with organizations in your industry or related fields can stimulate innovation through the exchange of ideas, technologies, and best practices.
Types of Partnerships in Agribusiness
Supplier Partnerships: These partnerships involve working closely with suppliers to ensure a reliable source of quality inputs, such as seeds, fertilizers, or animal feed.
Distributor and Retailer Partnerships: Collaborating with distributors and retailers ensures that your products reach a wider audience and are readily available to consumers.
Farmers’ Cooperatives: Joining or forming cooperatives with fellow farmers can provide collective bargaining power, shared resources, and access to markets.
Research and Development Partnerships: Partnering with research institutions or universities can lead to innovation in farming techniques, crop varieties, or sustainable practices.
Government and NGO Partnerships: Collaborating with government agencies and non-governmental organizations can offer support, grants, and expertise in areas like sustainability and compliance.
Strategies for Building Strong Partnerships
Now, let’s explore strategies for effectively building and maintaining strong partnerships in food and agribusiness management:
Clear Communication: Establish open and transparent communication channels with your partners. Clear communication is the foundation of any successful partnership.
Mutual Goals: Ensure that both parties have aligned goals and expectations from the partnership. This clarity prevents misunderstandings down the road.
Shared Values: Seek partners whose values and ethics align with your business. Shared values create a stronger foundation for collaboration.
Contracts and Agreements: Document the terms and responsibilities of the partnership in written agreements or contracts to avoid disputes in the future.
Continuous Engagement: Regularly engage with your partners, not just when issues arise. Building relationships takes ongoing effort.
Problem Solving: Approach challenges and conflicts as opportunities for problem-solving together rather than as reasons to terminate the partnership.
Evaluation: Periodically evaluate the effectiveness of the partnership and make adjustments as needed to ensure it remains mutually beneficial.
Building strong partnerships is a cornerstone of successful food and agribusiness management. Collaborating with suppliers, distributors, fellow farmers, and industry stakeholders can provide access to resources, reduce risks, and open doors to new opportunities. By nurturing these relationships with clear communication, shared goals, and a commitment to mutual success, you can create a thriving agribusiness in a dynamic and interconnected industry.
7. Risk Management
Risk Management in Food and Agribusiness: A Key to Sustainability and Success
In the world of food and agribusiness management, effective risk management is not just a good practice; it’s a critical necessity. The agriculture sector faces various risks, from unpredictable weather patterns to market volatility. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of risk management and strategies to protect your agribusiness.

Understanding Risk in Agribusiness
Agribusiness is inherently exposed to numerous risks, including:
Weather Risks: Unpredictable weather events, such as droughts, floods, or frost, can significantly impact crop yields and livestock production.
Market Risks: Commodity prices are subject to fluctuations due to supply and demand dynamics, international trade policies, and other market forces.
Pest and Disease Risks: Insects, diseases, and pests can devastate crops and livestock, leading to substantial losses.
Financial Risks: Economic downturns, changes in interest rates, and currency exchange rate fluctuations can affect the financial stability of agribusinesses.
Regulatory Risks: Changing regulations related to agriculture and food safety can lead to compliance challenges and increased operational costs.
Supply Chain Risks: Disruptions in the supply chain, such as transportation delays or supplier issues, can impact production and distribution.
The Importance of Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial for several reasons:
Minimizing Losses: By identifying and mitigating potential risks, you can reduce the impact of adverse events on your agribusiness.
Sustainability: Managing risks contributes to the long-term sustainability of your operation by ensuring consistent production and financial stability.
Competitive Advantage: Agribusinesses that proactively manage risks are better equipped to adapt to changing conditions and maintain a competitive edge.
Investor and Lender Confidence: Financial institutions and investors often require evidence of robust risk management practices to provide funding or support.
Strategies for Risk Management in Agribusiness
Now, let’s explore strategies for effectively managing risks in food and agribusiness management:
Diversification: Diversify your crops or product lines to spread risk. If one area is affected by adverse conditions, others may remain unaffected.
Insurance: Invest in crop, livestock, or business interruption insurance to protect against weather-related and other unforeseen risks.
Financial Planning: Maintain a financial cushion or contingency fund to cover unexpected expenses during challenging times.
Risk Assessments: Regularly assess your operation’s vulnerability to different risks and develop mitigation plans.
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and global factors that could impact commodity prices.
Sustainable Practices: Implement sustainable farming and business practices to reduce the environmental impact and enhance resilience.
Legal Compliance: Stay updated on and comply with regulatory changes to avoid fines or legal issues.
Emergency Preparedness: Develop contingency plans for potential disasters, including natural events and disease outbreaks.
Technology Adoption: Embrace technology for better weather forecasting, data analytics, and precision agriculture to optimize resource use.
Professional Advice: Consult with experts, such as agronomists, financial advisors, and legal counsel, to make informed decisions.
Effective risk management is a fundamental aspect of food and agribusiness management. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks in your operation, you can protect your business from adverse events, ensure long-term sustainability, and maintain a competitive edge in a dynamic industry. In agribusiness, being prepared for the unexpected is a key ingredient for success.
8. Focus on Quality Control
Focus on Quality Control in Food and Agribusiness Management
Quality control is a cornerstone of success in the world of food and agribusiness management. Ensuring consistent, high-quality products not only satisfies customer expectations but also contributes to your agribusiness’s reputation and profitability. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of quality control and strategies to maintain and improve it.

The Significance of Quality Control
Quality control in agribusiness involves a systematic process of monitoring and managing all aspects of production, from planting and harvesting to processing and distribution, to deliver products that meet or exceed established quality standards. Here’s why it’s crucial:
Customer Satisfaction: Consistently providing high-quality products leads to satisfied customers who are more likely to become loyal and repeat buyers.
Market Reputation: A reputation for quality sets your agribusiness apart from competitors and enhances brand trustworthiness.
Reduced Waste: Quality control helps minimize product defects and waste, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
Compliance: Meeting quality standards is often a requirement for accessing certain markets and complying with food safety regulations.
Strategies for Quality Control in Agribusiness
Now, let’s explore strategies to implement and enhance quality control in your food and agribusiness management:
Establish Quality Standards: Define clear quality standards for your products. These standards should cover aspects such as size, appearance, taste, and safety.
Training and Education: Train your workforce in quality control processes and ensure that they understand the importance of their role in maintaining quality.
Regular Inspection: Conduct regular inspections at every stage of production, from planting and harvesting to processing and packaging. This ensures that quality is maintained throughout the supply chain.
Testing and Analysis: Utilize laboratory testing and analysis to verify the quality of your products, especially for safety-critical aspects such as pesticide residues or pathogens.
Supplier Evaluation: Assess and monitor the quality of inputs and raw materials from your suppliers. Strong supplier relationships can lead to consistent quality.
Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of production and quality control processes. These records are invaluable for tracking and improving quality over time.
Continuous Improvement: Implement a culture of continuous improvement. Use feedback and data analysis to identify areas where quality can be enhanced.
Consumer Feedback: Encourage customers to provide feedback about your products. This feedback can help you identify issues and make necessary improvements.
Certifications: Consider obtaining quality certifications, such as ISO or organic certifications, to demonstrate your commitment to quality to customers and partners.
Food Safety Protocols: Implement food safety protocols, including HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), to prevent contamination and ensure product safety.
Quality Control and Sustainability
It’s worth noting that quality control and sustainability often go hand in hand. Sustainable practices, such as responsible water use, soil health management, and eco-friendly packaging, contribute to product quality and consumer trust.
Quality control is non-negotiable in food and agribusiness management. By prioritizing and continuously improving quality standards, you not only meet customer expectations but also safeguard your business’s reputation and long-term success. In a competitive industry, a commitment to delivering top-quality products can be a key differentiator and driver of growth for your agribusiness.
9. Employee Training and Development
Employee Training and Development: Nurturing Excellence in Food and Agribusiness Management
In the dynamic world of food and agribusiness management, your workforce is one of your most valuable assets. Investing in employee training and development is not just a responsibility; it’s a strategic move that can lead to improved productivity, innovation, and overall success. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of employee training and development and how it can benefit your agribusiness.

The Significance of Employee Training and Development
Employee training and development encompass a range of activities designed to enhance the skills, knowledge, and abilities of your workforce. Here’s why it’s crucial in food and agribusiness management:
Skills Enhancement: Ongoing training keeps your employees up-to-date with the latest industry practices and technologies, ensuring they can perform their roles effectively.
Innovation: A well-trained workforce is more likely to contribute fresh ideas, problem-solving skills, and innovation to your agribusiness.
Adaptability: Training helps employees adapt to changes in the industry, such as new regulations, sustainability practices, or emerging market trends.
Productivity: Skilled employees are more efficient and can contribute to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Employee Engagement: Providing development opportunities demonstrates your commitment to your employees’ growth, leading to higher job satisfaction and retention rates.
Quality Control: A trained workforce can maintain product quality and safety standards, reducing the risk of costly errors and recalls.
Strategies for Employee Training and Development
Now, let’s explore strategies to effectively invest in employee training and development in your food and agribusiness management:
Needs Assessment: Identify the specific skills and knowledge gaps within your workforce. This assessment serves as a foundation for targeted training.
Continuous Learning Culture: Foster a culture of continuous learning, where employees are encouraged to seek knowledge and skill development on an ongoing basis.
Training Programs: Develop training programs that address the identified needs. These can include workshops, online courses, on-the-job training, and external certifications.
Mentorship and Coaching: Pair experienced employees with newcomers to provide mentorship and guidance. This can accelerate the learning process.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback channels where employees can provide input on training programs and suggest areas for improvement.
Recognition and Rewards: Recognize and reward employees who actively participate in training and demonstrate newly acquired skills.
Leadership Development: Invest in leadership development programs to nurture future leaders within your organization.
Cross-Training: Encourage employees to broaden their skills by learning about different aspects of agribusiness. Cross-training can enhance versatility and problem-solving abilities.
Online Learning Platforms: Utilize online learning platforms and resources to provide flexible, accessible training options for your workforce.
Safety Training: Prioritize safety training to protect employees and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Measuring the Impact
To gauge the effectiveness of your training and development initiatives, consider metrics such as improved productivity, reduced errors, increased employee satisfaction, and enhanced innovation.
In conclusion, employee training and development are essential components of food and agribusiness management. By investing in your workforce’s skills and knowledge, you empower them to contribute to the success and growth of your agribusiness. In a rapidly changing industry, a well-trained and engaged workforce can be a powerful competitive advantage and a key driver of excellence.
Read, Also >>>>> Discover The Top 10 Common Plant Diseases in Organic Farming and How to Beat Them
10. Adaptability and Innovation
Adaptability and Innovation: Thriving in the Evolving Landscape of Food and Agribusiness
In the ever-changing world of food and agribusiness management, adaptability and innovation are not just buzzwords; they’re fundamental strategies for success. Embracing change and fostering a culture of innovation can help your agribusiness navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and stay competitive. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of adaptability and innovation and how they can benefit your agribusiness.

The Significance of Adaptability and Innovation
Adaptability and innovation are closely intertwined and play pivotal roles in food and agribusiness management:
Adaptability:
In a sector where external factors like climate, market conditions, and regulations are in constant flux, the ability to adapt is essential. Being adaptable means responding effectively to change, whether it’s in production methods, supply chain management, or consumer preferences.
Innovation:
Innovation is the engine that drives progress in agribusiness. It involves creating and implementing new ideas, technologies, and practices to improve efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness. Innovations can encompass everything from crop varieties and farming techniques to packaging and distribution methods.
Benefits of Adaptability and Innovation
Resilience: An adaptable agribusiness can withstand unforeseen challenges, such as weather-related disasters or market fluctuations, without compromising its ability to function.
Competitive Advantage: Innovative practices and products set your agribusiness apart from competitors. They can attract new customers, open new markets, and increase market share.
Sustainability: Innovation can lead to more sustainable farming and business practices, helping to conserve resources and reduce environmental impact.
Efficiency: Innovations often lead to increased operational efficiency, which can reduce costs and enhance productivity.
Problem-Solving: Innovative thinking enables your team to tackle complex problems and find creative solutions.
Strategies for Adaptability and Innovation
Now, let’s explore strategies to foster adaptability and innovation in your food and agribusiness management:
Cultivate a Growth Mindset: Encourage your team to embrace change and view challenges as opportunities for growth and improvement.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Create a culture of collaboration where team members from various departments share ideas and insights.
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends, consumer preferences, and emerging technologies that could impact your industry.
Invest in Research and Development (R&D): Allocate resources to R&D activities that explore new technologies and farming practices.
Pilot Projects: Experiment with pilot projects to test new ideas or innovations on a smaller scale before full implementation.
Feedback Channels: Establish feedback mechanisms that encourage employees to share their ideas and provide input on improving processes.
Training and Skills Development: Invest in training and development programs that enhance employees’ skills and encourage innovative thinking.
Networking: Attend industry events, conferences, and trade shows to connect with innovators and stay updated on the latest developments.
Risk-Taking: Create an environment where calculated risks are encouraged, knowing that some level of risk is often necessary for innovation.
Recognition and Rewards: Recognize and reward employees for innovative contributions to foster a culture of innovation.
In conclusion, adaptability and innovation are essential for success in food and agribusiness management. By embracing change, seeking new opportunities, and fostering a culture of innovation, you can position your agribusiness to thrive in a dynamic and competitive industry. In the face of challenges and uncertainty, adaptability and innovation are your keys to resilience and long-term growth.
Read, Also >>>>> Discover The Top 10 Common Plant Diseases in Organic Farming and How to Beat Them












2 replies on “Discover The 10 Proven Strategies for Successful Food and Agribusiness Management”
[…] Read, Also >>>>>> Discover The 10 Proven Strategies for Successful Food and Agribusiness Management […]
[…] Read, Also >>>>>>> Discover The 10 Proven Strategies for Successful Food and Agribusiness Management […]